Google has generously offered free hosting services for free open source developers to host their projects either by using Mercurial, Subversion or git.
This blog post touches on the basic on to use SVN to maintain source code repository on Google Code Hosting.
Assumptions
This tutorial assume that you have :
- Created an open source project on Google Code
- Installed subversion on your GNU/Linux operating system
- Have source code to import
Initial Import
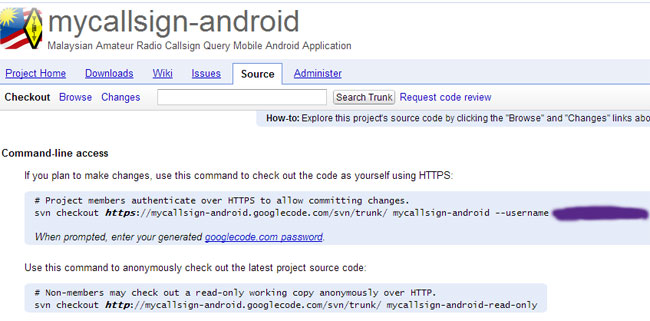
You must perform initial check-in in order to use the SVN repository. To do that, you must go to your Google Code project, as shown in the screenshot.
From bash terminal, to import your project into Google Code, type:
svn import /path-to/src/ https://your-project-name.googlecode.com/svn/trunk/ --username example@gmail.com -m "initial import"
You'll be prompted to enter googlecode.com password, which you can generate from your Google project page
SVN commit
After initial import, your source code will be made available from Google Code hosting for public access.
You may 'commit' after you've made revision or alteration into the source code. to "commit" type:
[bash]
svn commit -m "added new TextField to user-interface"
[/bash]
the -m specifies change log, you shouldn't commit without a proper log message as this will help other users to track the changes that you've made with your source code.
SVN add: For adding new source files
If you add new files to your source code, just type:
[bash]
svn add <filename>
[/bash]
You may then proceed with "svn commit" to add the file to the repository server.
Recursively add unversioned files into SVN repository
If you've added several new files into source code working copy, these file will be unversioned and thus won't be committed to the subversion server.
You can use this command recursively add new unversioned files to svn repository.
[bash]
svn status | perl -ne 's/^\?\s+(\S.+)$/\1/g;chomp;system("svn add \"$_\"");'
[/bash]
**taken from http://www.amiryan.org/2009/04/22/howto-recursively-add-unversioned-files-into-svn-repository/