The month of April is here and beside fooling your friends on the first of april, let me remind you that Ubuntu Linux (7.04) Feisty Fawn release is just around the corner.
Schedule to be released on April 19, 2007. Free Ubuntu Feisty Fawn CDs is suspected to be back available from ShipIt!
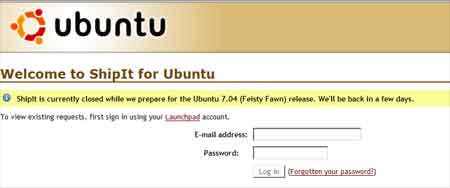
Here’s the screenshot ShipIt interface.
What is Shipit?
For those who are unfamiliar with the term, ShipIt is a service maintained by the Ubuntu project for the purpose of shipping free Ubuntu CD through out the world.
To order free CDs, you need to have a launchpad account and the CDs will take around 1-6 weeks to arrive, depending on where you live (and customs delays).
PowerPC CD won’t be available ?
Also it is worth noting that Ubuntu has dropped PowerPC platform from its official release, so the usual PowerPC CD won’t be available from Shipit as with previous releases.
[tags]powerpc,ubuntu,feisty,feisty fawn, debian,linux, opensource,open source[/tags]