Linux comes in many flavors or distros, and each distro handles software installation differently from one another. Most GNU/Linux distro uses a package management system to manage software updates/instalation/removal in order to help users administer their Linux systems.
However, many of these package management system has different interface and commands, as such users from Ubuntu (or Debian based) might only be familiar with ‘apt’ or dpkg while Fedora (Red Hat based) users might only familiar with yum and rpm, which may create confusion when users from either distro were to exchange environments.
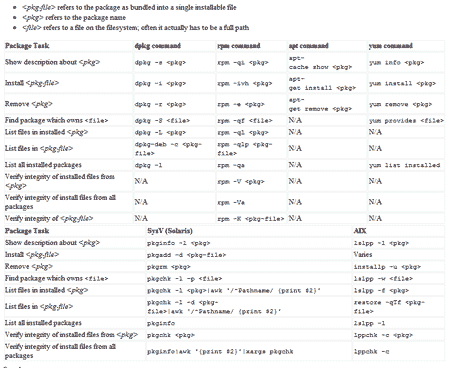
Luckily, somebody was kind enough to provide these users with Linux Package Manager Cheat Sheet which act as a reference point whenever a user had to switch to another distro which uses package management that are not familiar with them.
The package management software listed are for: apt,dpkg,yum, rpm, pkg* (slackware based) and AIX-based lsl**.
[ Source ]