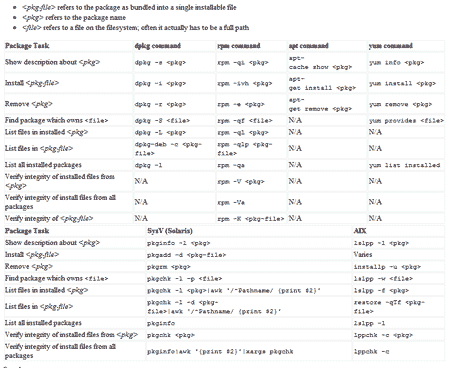
Httrack is a tool for copying and saving an entire website in Debian and Ubuntu. Httrack can crawl an online website save each of the pages (including graphic and other downloadable files).
Among httrack features are:
- Able to continue interrupted downloads
- Selective download
- Customizable user-agent
- Customizable Scan-rules, can exclude files from being crawled
- Accept cookies
- URL hacks
- Tolerant requests support
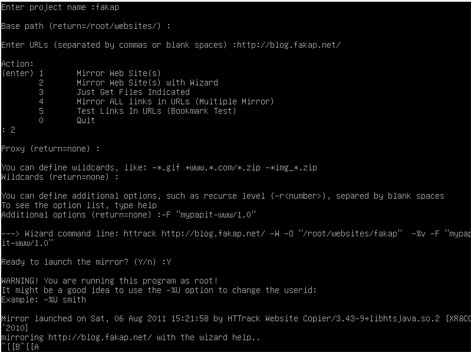
Using ‘httrack‘ is easy, as it has built-in wizard that can guide you through the process of mirroring web sites. The user will be asked a series of question about the URL to be mirrored, the location where the files will be saved, proxy server and the user-agent to be used.
p/s: httrack perhaps is the only open-source website copier/downloader tool available for GNU/Linux operating system. It is efficient and easy to use. The only gripe that I’ve when using ‘httrack‘ is that it does not provide progress feedback (unlike its counterpart in Microsoft Windows) like ‘wget‘