Wow, I never know that strace can be used as a poor man’s ssh keylogger – Poor Man’s SSH Keylogger
How to add contrib and non-free repository in Debian GNU/Linux
Debian GNU/Linux is probably the only Linux distro that has the largest software repository. However the default installation for Debian only includes the ‘main’ repository which is directly maintained by the Debian community and fulfills the Debian Free Software Guidelines (DFSG).
The two other repositories ‘contrib’ and ‘non-free’ are not enabled by default as it contains software that either does not meet DFSG requirements or depends on library or packages which does not meet DFSG requiments.
How to enable contrib and non-free repo in Debian
As ‘root’ you need to edit /etc/apt/sources.lst
Then add ‘contrib’ and ‘non free’ at the end of each line that begins with “deb” and “deb-src” just like the example:
deb http://http.us.debian.org/debian jessie main contrib non-free deb http://security.debian.org jessie/updates main contrib non-free
Save the file, and run ‘apt-get update‘ and optionally ‘apt-get upgrade‘ to activate the changes.
Recommended Reading
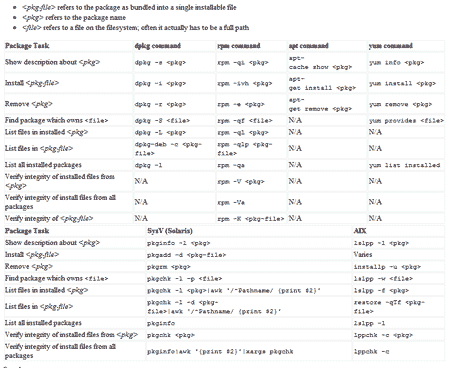
Linux Package Manager Cheat Sheet Reference Chart
Linux comes in many flavors or distros, and each distro handles software installation differently from one another. Most GNU/Linux distro uses a package management system to manage software updates/instalation/removal in order to help users administer their Linux systems.
However, many of these package management system has different interface and commands, as such users from Ubuntu (or Debian based) might only be familiar with ‘apt’ or dpkg while Fedora (Red Hat based) users might only familiar with yum and rpm, which may create confusion when users from either distro were to exchange environments.
Luckily, somebody was kind enough to provide these users with Linux Package Manager Cheat Sheet which act as a reference point whenever a user had to switch to another distro which uses package management that are not familiar with them.
The package management software listed are for: apt,dpkg,yum, rpm, pkg* (slackware based) and AIX-based lsl**.
[ Source ]
Bitcoin spending and transaction can be traceable
It seems that Bitcoin is only designed to eliminate the need for centralized issuer and central authority, but not anonymity, which is a common misconception among internet users as according to one of its developers (Jeff Garzik), transaction is recorded in public log and although the identity of the parties involved can’t be directly identified, the transaction can be easily traced and linked to other accounts through data mining and statistical analysis.
So it is harder to stay anonymous in transactions that involve large currency value.
 Bitcoin is not anonymous
Bitcoin is not anonymous
How to optimize MySQL tables automatically using cron
Busy websites which has a lot of insert/delete transactions may introduce fragmentation in MySQL tables. Fortunately, users and optimize mysql tables with ‘OPTIMIZE TABLE’ command, but how to execute it automatically?
Here’s how:
The mysql-client package in Ubuntu installation comes with a tool called mysqlcheck which is handy for optimizing table in mysql. This command can be executed from bash and can be executed using cron.
to do that, just run this command.
[bash]
cron -e
#in the crontab file– add this line
59 23 * * * /usr/bin/mysqlcheck -o -v -u <mysql username> -h localhost <database_name> -p <password>
[/bash]
This will tell cron to execute mysqlcheck and optimize mysql table of the specified database exactly on 11:59pm, every day. You can change the setting to suit your need.
How to change hostname in Ubuntu server
Here’s how you can change hostname in Ubuntu server
1. Edit /etc/hostname, and change the hostname
2. Edit /etc/hosts file, and add the hostname to 127.0.0.1, or to any local machine ip
3. run, “sudo server hostname stop”, and “sudo server hostname start”